What is a business cycle?
The phases of the economic cycle
BBVA 2% Deposito Flessibile for 12 months
How long does an economic cycle last?
There is no defined and circumscribed duration for each phase, nor for the overall cycle, but the statistical analyzes on historical data have allowed us to establish an average duration of the cycles, classified as follows:
- Short, or Kitchin cycles with an average duration of 40 months, do not necessarily reach the stage of depression. Typically, they are associated with specific sectors in which, for example, there is a change in consumer preferences but the Companies are not aligned (e.g. lack of production processes).
- Medium, or Juglar cycles, with an average duration of 8-10 years. They are distinguished by the presence of cyclical expansions and crises. They could be defined as a succession of short economic cycles at the end of which the market fails to "recover" completely. It is not uncommon for them to end in a structural crisis with significant impacts on all economic areas.
- Long, long waves or Kondratieff cycles, lasting around 50-60 years. During the expansion, the ascents are more prolonged and stronger, the crises are lighter and the recessions shorter; but during the depression the recovery movements are weak and brief, resulting in increasingly strong crises and prolonged recessions, until reaching the degree of general economic depressions that in contemporary economies typically translate into economic declines on a global scale.
Esistono numerosi studi sui cicli economici tra i quali particolarmente di rilievo quello di Ralph Nelson Elliott che, a partire dall’osservazione delle fluttuazioni della Borsa valori crea un modello tuttora utilizzato dagli analisti finanziari. The economist noted the presence of "waves" within each economic cycle, from the longest to the shortest: the underlying principle is that every action has an equal and opposite reaction and that this dynamic is reflected in the wave trend of the economic dynamics. Each economic cycle would therefore be composed of eight curves of which the first 5 describe the main market trend and the following 3 act as market corrections.
Controlla le tue finanze personali
Il ciclo economico di una famiglia o di una singola persona, riguarda l’alternanza che si può verificare all’interno delle proprie finanze e la capacità di stabilire un equilibrio tra entrate e uscite.
Per avere una certa stabilità e godere di maggiore tranquillità, bisogna essere previdenti. Tenere per esempio un salvadanaio online è un modo per accumulare piccoli risparmi. Inoltre, applicando delle semplici Regole automatiche di risparmio potrai far crescere i tuoi risparmi senza sforzi.
Se vuoi sapere di più sul risparmio, nella sezione di Benessere finanziario del nostro blog, troverai tanti consigli utili per pianificare al meglio le tue finanze e raggiungere i tuoi obiettivi di risparmio.
Dai vita ai tuoi progetti con soluzioni su misura per i tuoi obiettivi di risparmio e investimento.
You might be interested
-
It is a 3 or 4 digit numerical code. It is used as a security tool in transactions where the card is not physically used, such as when shopping online.
-
Features of credit, debit, and prepaid cards: find out how they work and choose the one that best suits your needs.
-
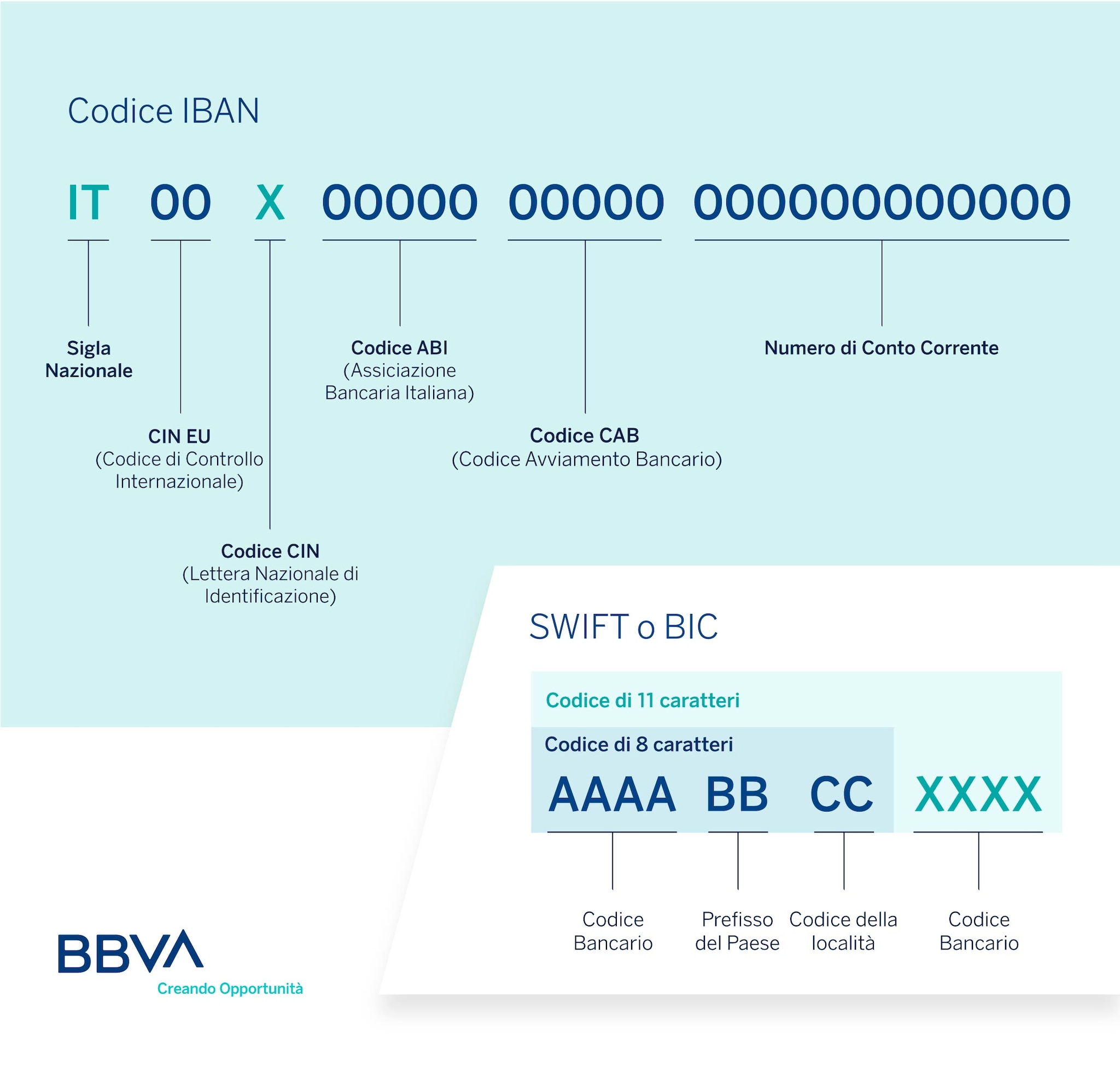
The IBAN code is the identification code of the current account number. The BIC or SWIFT code, on the other hand, is the one that corresponds to the banking institutions and branches.